normal end tidal co2 after intubation
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. Consistent waveform and end-tidal CO2 20 kPa.

Capnography Best Practices To Improve Patient Handoff Reports Capnoacademy Capnoacademy
Waveform capnography should be monitored in all intubated patients and displayed on the monitor as above.
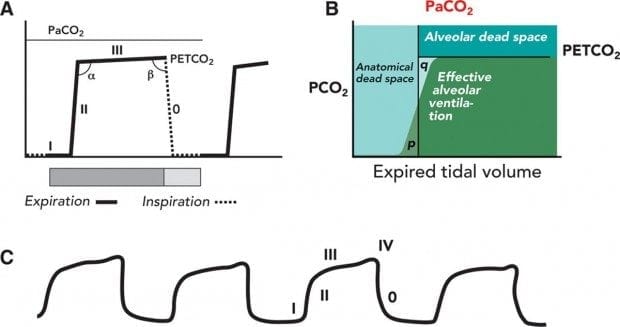
. As effective CPR leads to a higher cardiac output ETCO2 will rise reflecting the increase in perfusion. The indicator is purple which indicates failure to detect CO2. The median time for ETCO 2 to reach 4 mm Hg was 53 range 0727 s and to reach 15 mm Hg was 81 range 0827 s.
Annals of emergency medicine 2005. To our knowledge this is the first airway management trial in which end-tidal oxygen concentration EtO 2 has been used as a surrogate outcome for patient oxygenation status during intubationEtO 2 the oxygen concentration at the end of an exhaled breath reflects the oxygen concentration in the alveolar space an important determinant of the arterial partial. End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest.
Rapid Sequence Intubation Figure 1-3 End-tidal CO2 detector before application. In these cases waveform morphology was normal and continued to the 2 min cessation point. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function.
The second intubation showed a normal end-tidal carbon dioxide wave form that declined over a minute accompanied by decreasing oxygen saturation. What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2. Return of spontaneous circulation.
A prospective clinical trial was conducted at a level I trauma center to assess the efficacy of end-tidal carbon dioxide CO2 detection in four groups of patients requiring emergency intubation because of cardiac arrest major trauma respiratory failure or. Misting increased SaO2 Types of End-Tidal CO2 Qualitative Yes or No. The median time for detection of ETCO 2 following intubation was 37 range 044 s.
The presence of a normal waveform denotes a patent airway and spontaneous breathing. We have previously demonstrated life-like end-tidal capnography ETCO 2 waveforms following tra-cheal intubation of two fresh-frozen cadavers1 This has highlighted the potential for use of cadavers in airway management simulation training. The use of quantitative end-tidal capnometry to avoid inadvertent severe hyperventilation in patients with head injury after paramedic rapid sequence intubation.
Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. The effectiveness of out-of-hospital use of continuous end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring on the rate of unrecognized misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services system.
Videos of the waveforms are available as online supplementary files numbers 18. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a capnometer. 56 End-tidal CO 2 does evaluate effectiveness of ventilation but it is also dependent on cardiacoutputtodeliverCO 2 tothepulmonarysystemTherefore adysfunctionineithertherespiratoryorcardiacsystemcancause a variation in ETCO 2 readings.
Bhende M End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in pediatrics-clinical applications. End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. For two cadavers life-like ETCO 2 waveforms were achieved immediately after tracheal intubation with maximum ETCO 2 achieved by the second breath.
Norm al EtCO2 levels 46 to 60 kPa signify adequate perfusion. End-tidal CO2 diminishes over time Sudden increase in ETCO2. Finally the endotracheal tube was found to be in the esophagus at postmortem.
Normal end tidal co2 after intubation Monday March 21 2022 Edit EtCO2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of CO2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the alveolar CO2 concentration. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. The time taken for intubation was not significantly related to the time for ETCO 2 to be detected r016 p022.
It can be challenging to make the clinical decision when to terminate resuscitative efforts when caring for a patient experiencing cardiac. 2 to near normal normal EtCO 2 35-45 mmHg represents marked increase of CO 2 delivery to lungs suggesting ROSC If patient develops an organized rhythm after VFVTasystole check EtCO 2 to see if ROSC has occurred CONFIRM PLACEMENT OF ETT After intubation if ETCO 2 10mm Hg tube in trachea. The purpose of our study was to determine whether ETCO2 measurement could distinguish tracheal from esophageal tube.
End-tidal CO2 is also useful during resuscitation to help predict death after a prolonged cardiac arrest. It is pos-sible that carbon dioxide CO 2 remains in the lungs postmortem and is liberated by artificial ven-. In children with normal hearts and lungs ETCO 2 tension is normally within 2 to 5 mm Hg of PaCO2.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. Changes in the shape of the capnogram are diagnostic of disease conditions while changes in end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 the maximum CO 2 concentration at the end of each tidal breath can be used to assess disease severity and response to treatment. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
EtCO2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of CO2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the alveolar CO2 concentration. After 20 minutes of CPR an end-tidal CO2 level of 19 mm Hg or less is predictive of death as an outcome of the cardiac arrest. Capnography can be used to assess unresponsive patients ranging from those are actively seizing to victims of chemical terrorism.
This is t he appearance when the esophagus is intubated. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector End tidal CO2 detector Secondary signs. Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values.
With previously normal pCO 2 or acute rise of 10 or more torr. Measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 has been used to detect accidental esophageal tube placement in noncardiac arrest situations.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
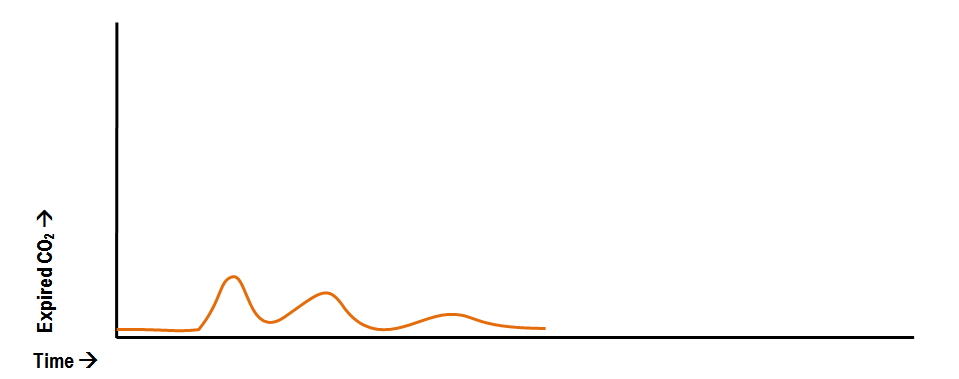
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography Nursing Procedures Icu Nursing Nursing School Studying

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

End Tidal Co2 Respiratory Therapy Tidal Co2

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
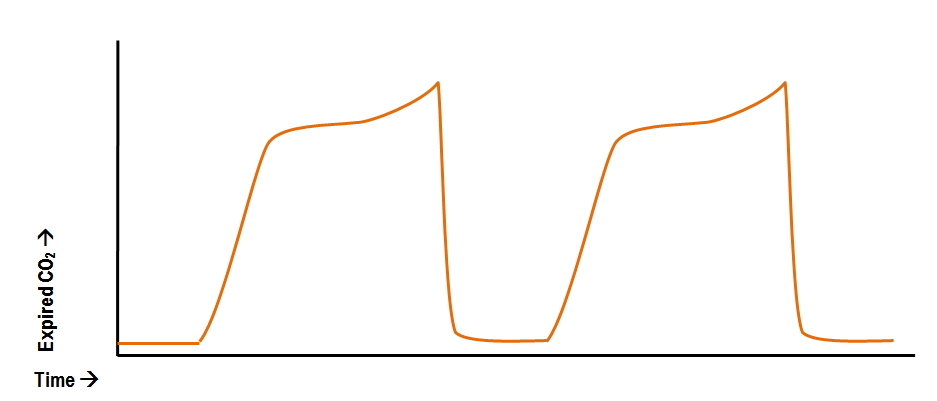
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

